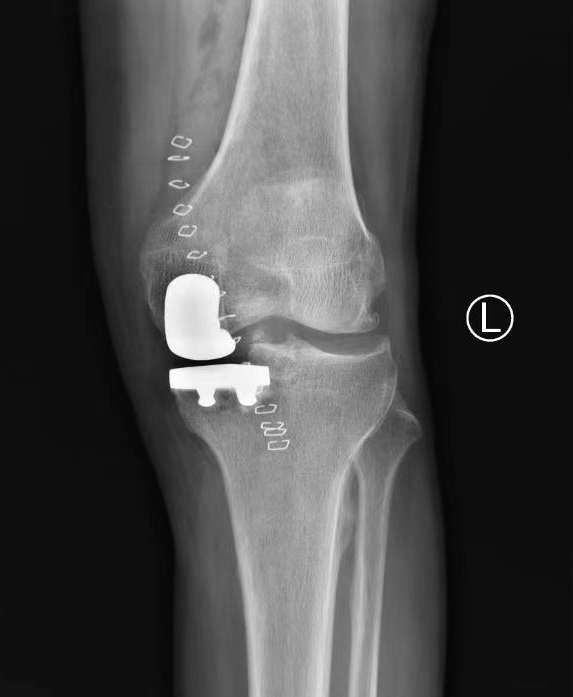
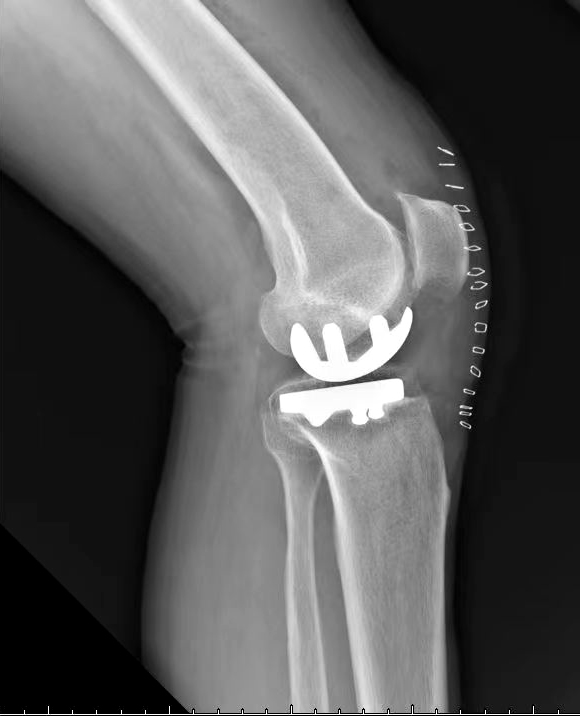
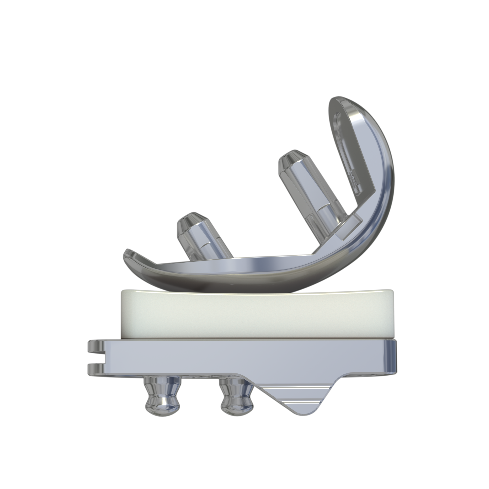
Recently, Director Chengjie Liao of Northeast International Hospital performed a “bilateral” unicondylar replacement surgery for a patient with bilateral knee osteoarthritis with a LDK XU UKA prosthesis, and the surgery went well.
The patient had been suffering from pain in both knees for 10 years and had pain when walking. After completing the relevant examinations, Director Chengjie Liao found that both knees were eligible for unicondylar replacement, so he decided to perform bilateral knee unicondylar replacement to preserve the original function of the knee to a greater extent.
Bilateral replacement and precise knee preservation successfully solved the patient’s bilateral knee pain problem, and the patient was very satisfied with the surgical result.
Description:
Patient, male, 60 years old
Complaint:
Pain in bilateral knee joints for 10 years, aggravated for recent 2 months.
Current medical history:
The patient had pain in both knees 10 years ago, pain when walking, the left knee was slightly severe, with the medial side being worse, no significant restriction in flexion and extension activities, the pain was obvious when walking with the medial side of both knees, the pain has increased in the last 2 months, the effect of oral painkillers was not good, for further treatment admitted to the hospital
Past history:
Hypertension for 3 years.
Physical check:
Normal physiological curvature of the spine, no pressure on the spinous processes of the lumbar spine, no swelling of both knees, no obvious inversion deformity, normal flexion and extension of both knees, pressure pain around the left knee (+), with medial pain as obvious, positive patellar grinding test, negative floating patella test, negative drawer test, knee mobility: left knee flexion 120°, extension 0°, right knee flexion 120°, extension 0°
Auxiliary examinations:
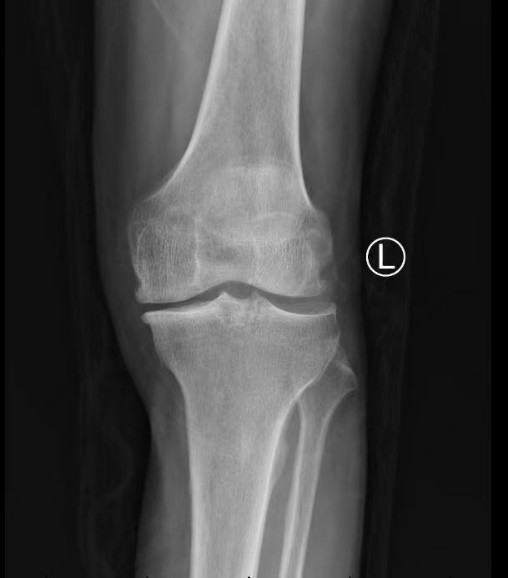
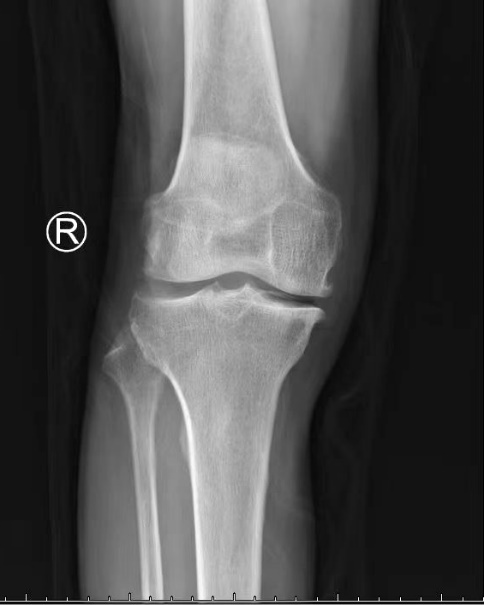
Frontal and lateral x-ray of the left knee showed osteophytes on the margins of the bones of the left knee joint, the intercondylar ridge became sharp, some of the articular surfaces were sclerotic with osteophytes, and the joint space was slightly narrowed.
Frontal and lateral X-rays of the right knee showed sharp osteophytes at the edges of the bones of the right knee joint, the intercondylar ridge became sharp, the joint surface was sclerotic with osteophytes, and the joint space became narrow.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the left knee showed: sagittal T2WI-FS, coronal T1WI T2WI-FS, and transverse T2WI images: osteophytes and osteophytes in the left knee, narrowing of the medial joint space, thinning of the articular cartilage, irregularity and partial absence, patchy high signal under the joint surface of the distal femur and proximal tibia, and round-like cystic signal in the proximal tibia. The FS images of the medial and lateral meniscus showed linear high signal. The posterior horn of the medial meniscus was irregularly shaped and displaced, and the high signal extended to the edge. The anterior cruciate ligament was thickened with increased FS image signal, and the FS image of the lateral collateral ligament showed linear high signal; the posterior cruciate ligament and the medial collateral ligament did not show any significant abnormal signal. The joint capsule was seen to be filled with fluid, and the caruncle was seen to be cystic. The FS images of the peripatellar soft tissue and the infrapatellar fat pad showed heterogeneous patchy high signal.
Magnetic resonance of the right knee showed: sagittal T2WI-FS, coronal T1WI T2WI-FS, and transverse T2WI images: osteophytes of all bones of the right knee, narrowing of the joint space, thinning of the articular cartilage, irregularity, partial absence, and patchy high signal under the joint surface of the distal femur and proximal tibia on FS images. The FS images of the medial and lateral meniscus showed linear high signal, and the medial meniscus was irregularly shaped and outwardly displaced. The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments had irregular morphology and showed heterogeneous high signal on FS image, while the medial and lateral collateral ligaments did not show any significant abnormal signal. Irregular fluid accumulation signal was seen in the joint capsule. The FS image of the peripatellar soft tissue and subpatellar fat pad showed heterogeneous patchy high signal.
Anterior X-ray of both hip joints showed: The bone density and morphology of the bones of both hip joints were not abnormal, and the joint space showed clear, no widening or narrowing, no exact fracture or signs of bone destruction were seen. There was no abnormality in the surrounding soft tissues.
Clinical diagnosis:
1. Osteoarthritis of both knees
2. Hypertension
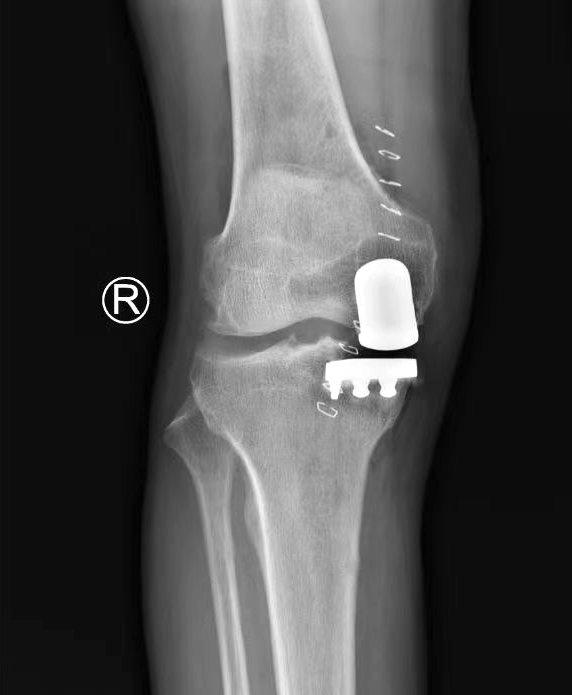
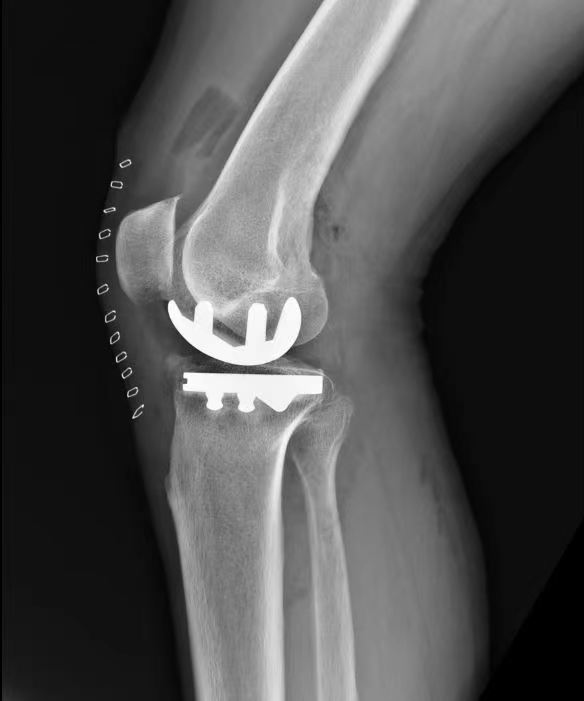
Postoperative:
XU UKA
LIAO Chengjie
Chief Physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Northeast International Hospital
Young member of Bone and Joint and Rheumatism Committee
of China Society of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Member of the first committee of the Liaoning Medical Association Traumatology Branch,
Member of Liaoning Provincial Osteoporosis Professional Committee.
Post time: Apr-19-2023